The two founders of Crusoe Energy think they may have a solution to two of the largest problems facing the planet today — the increasing energy footprint of the tech industry and the greenhouse gas emissions associated with the natural gas industry.
Crusoe, which uses excess natural gas from energy operations to power data centers and cryptocurrency mining operations, has just raised $128 million in new financing from some of the top names in the venture capital industry to build out its operations — and the timing couldn’t be better.
Methane emissions are emerging as a new area of focus for researchers and policymakers focused on reducing greenhouse gas emissions and keeping global warming within the 1.5 degree targets set under the Paris Agreement. And those emissions are just what Crusoe Energy is capturing to power its data centers and bitcoin mining operations.
The reason why addressing methane emissions is so critical in the short term is because these greenhouse gases trap more heat than their carbon dioxide counterparts and also dissipate more quickly. So dramatic reductions in methane emissions can do more in the short term to alleviate the global warming pressures that human industry is putting on the environment.
And the biggest source of methane emissions is the oil and gas industry. In the U.S. alone roughly 1.4 billion cubic feet of natural gas is flared daily, said Chase Lochmiller, a co-founder of Crusoe Energy. About two thirds of that is flared in Texas with another 500 million cubic feet flared in North Dakota, where Crusoe has focused its operations to date.
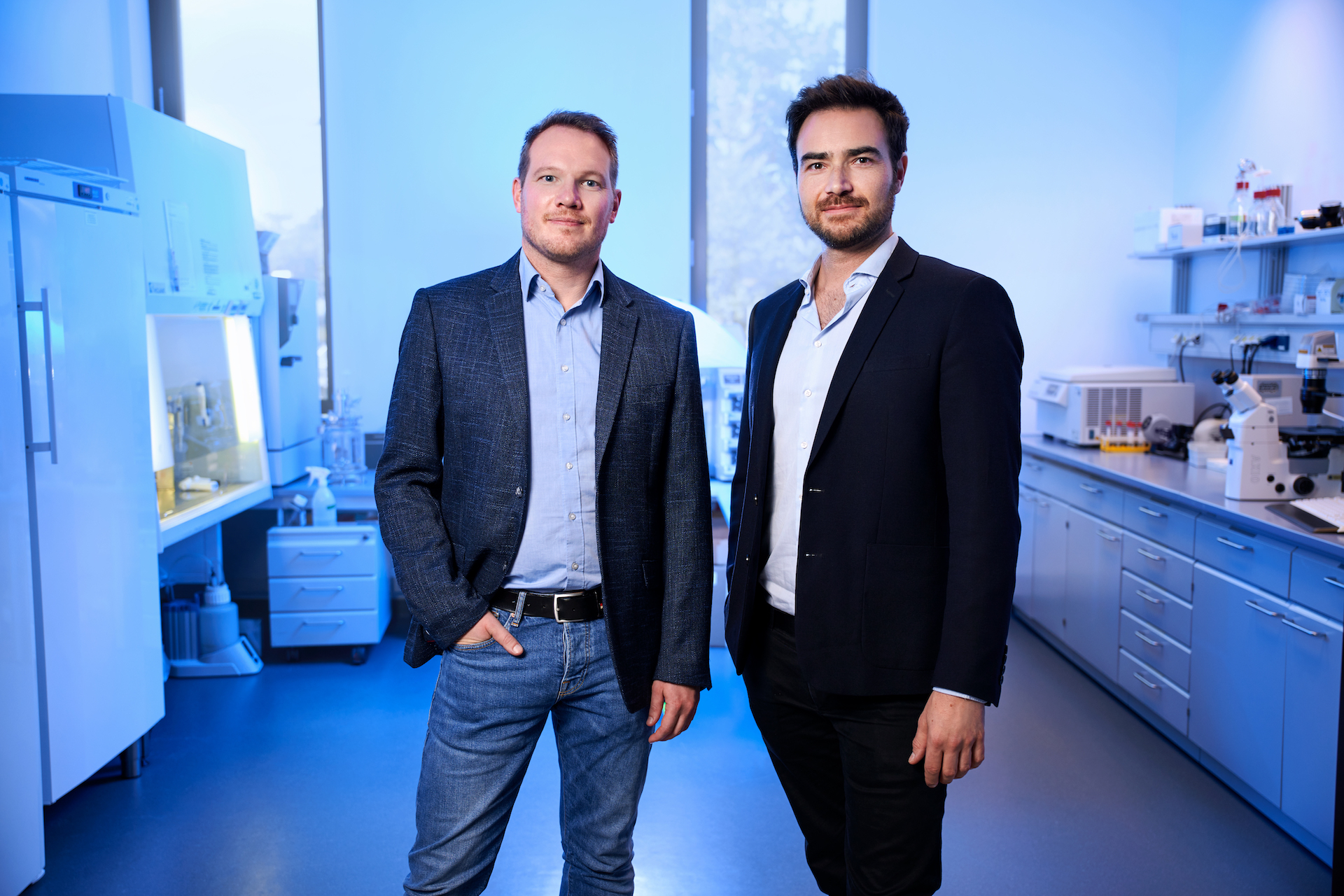
For Lochmiller, a former quant trader at some of the top American financial services institutions, and Cully Cavmess, a third generation oil and gas scion, the ability to capture natural gas and harness it for computing operations is a natural combination of the two men’s interests in financial engineering and environmental preservation.
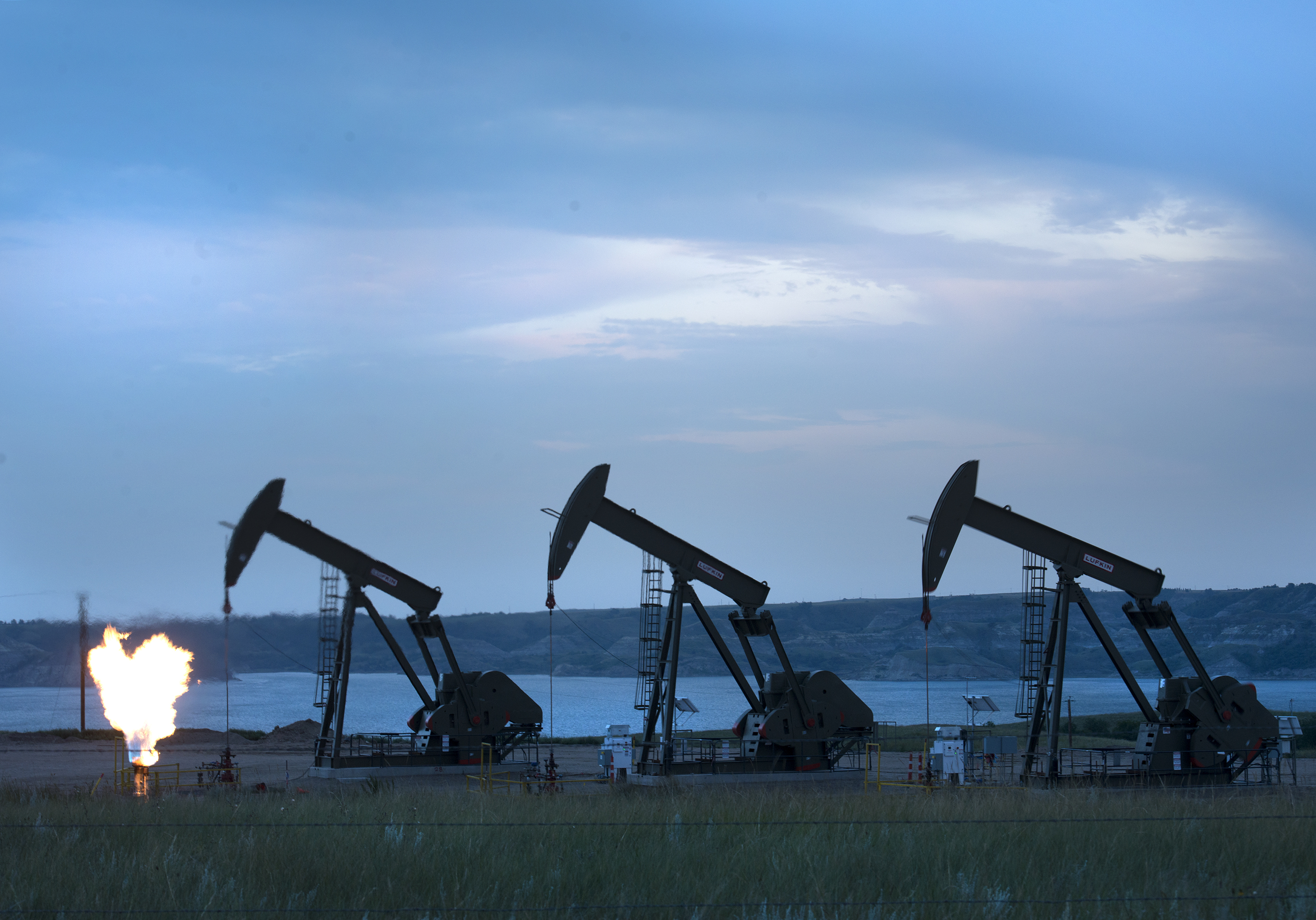

NEW TOWN, ND – AUGUST 13: View of three oil wells and flaring of natural gas on The Fort Berthold Indian Reservation near New Town, ND on August 13, 2014. About 100 million dollars worth of natural gas burns off per month because a pipeline system isn’t in place yet to capture and safely transport it . The Three Affiliated Tribes on Fort Berthold represent Mandan, Hidatsa and Arikara Nations. It’s also at the epicenter of the fracking and oil boom that has brought oil royalties to a large number of native americans living there. (Photo by Linda Davidson / The Washington Post via Getty Images)
The two Denver natives met in prep-school and remained friends. When Lochmiller left for MIT and Cavness headed off to Middlebury they didn’t know that they’d eventually be launching a business together. But through Lochmiller’s exposure to large scale computing and the financial services industry, and Cavness assumption of the family business they came to the conclusion that there had to be a better way to address the massive waste associated with natural gas.
Conversation around Crusoe Energy began in 2018 when Lochmiller and Cavness went climbing in the Rockies to talk about Lochmiller’s trip to Mt. Everest.
When the two men started building their business, the initial focus was on finding an environmentally friendly way to deal with the energy footprint of bitcoin mining operations. It was this pitch that brought the company to the attention of investors at Polychain, the investment firm started by Olaf Carlson-Wee (and Lochmiller’s former employer), and investors like Bain Capital Ventures and new investor Valor Equity Partners.
(This was also the pitch that Lochmiller made to me to cover the company’s seed round. At the time I was skeptical of the company’s premise and was worried that the business would just be another way to prolong the use of hydrocarbons while propping up a cryptocurrency that had limited actual utility beyond a speculative hedge against governmental collapse. I was wrong on at least one of those assessments.)
“Regarding questions about sustainability, Crusoe has a clear standard of only pursuing projects that are net reducers of emissions. Generally the wells that Crusoe works with are already flaring and would continue to do so in the absence of Crusoe’s solution. The company has turned down numerous projects where they would be a buyer of low cost gas from a traditional pipeline because they explicitly do not want to be net adders of demand and emissions,” wrote a spokesman for Valor Equity in an email. “In addition, mining is increasingly moving to renewables and Crusoe’s approach to stranded energy can enable better economics for stranded or marginalized renewables, ultimately bringing more renewables into the mix. Mining can provide an interruptible base load demand that can be cut back when grid demand increases, so overall the effect to incentivize the addition of more renewable energy sources to the grid.”
Other investors have since piled on including: Lowercarbon Capital, DRW Ventures, Founders Fund, Coinbase Ventures, KCK Group, Upper90, Winklevoss Capital, Zigg Capital and Tesla co-founder JB Straubel.
The company now operate 40 modular data centers powered by otherwise wasted and flared natural gas throughout North Dakota, Montana, Wyoming and Colorado. Next year that number should expand to 100 units as Crusoe enters new markets such as Texas and New Mexico. Since launching in 2018, Crusoe has emerged as a scalable solution to reduce flaring through energy intensive computing such as bitcoin mining, graphical rendering, artificial intelligence model training and even protein folding simulations for COVID-19 therapeutic research.
Crusoe boasts 99.9% combustion efficiency for its methane, and is also bringing additional benefits in the form of new networking buildout at its data center and mining sites. Eventually, this networking capacity could lead to increased connectivity for rural communities surrounding the Crusoe sites.
Currently, 80% of the company’s operations are being used for bitcoin mining, but there’s increasing demand for use in data center operations and some universities, including Lochmiller’s alma mater of MIT are looking at the company’s offerings for their own computing needs.
“That’s very much in an incubated phase right now,” said Lochmiller. “A private alpha where we have a few test customers… we’ll make that available for public use later this year.”
Crusoe Energy Systems should have the lowest data center operating costs in the world, according to Lochmiller and while the company will spend money to support the infrastructure buildout necessary to get the data to customers, those costs are negligible when compared to energy consumption, Lochmiller said.
The same holds true for bitcoin mining, where the company can offer an alternative to coal powered mining operations in China and the construction of new renewable capacity that wouldn’t be used to service the grid. As cryptocurrencies look for a way to blunt criticism about the energy usage involved in their creation and distribution, Crusoe becomes an elegant solution.
Institutional and regulatory tailwinds are also propelling the company forward. Recently New Mexico passed new laws limiting flaring and venting to no more than 2 percent of an operator’s production by April of next year and North Dakota is pushing for incentives to support on-site flare capture systems while Wyoming signed a law creating incentives for flare gas reduction applied to bitcoin mining. The world’s largest financial services firms are also taking a stand against flare gas with BlackRock calling for an end to routine flaring by 2025.
“Where we view our power consumption, we draw a very clear line in our project evaluation stage where we’re reducing emissions for an oil and gas projects,” Lochmiller said.