Qualcomm launches new AR dev kit, acquires Clay AIR
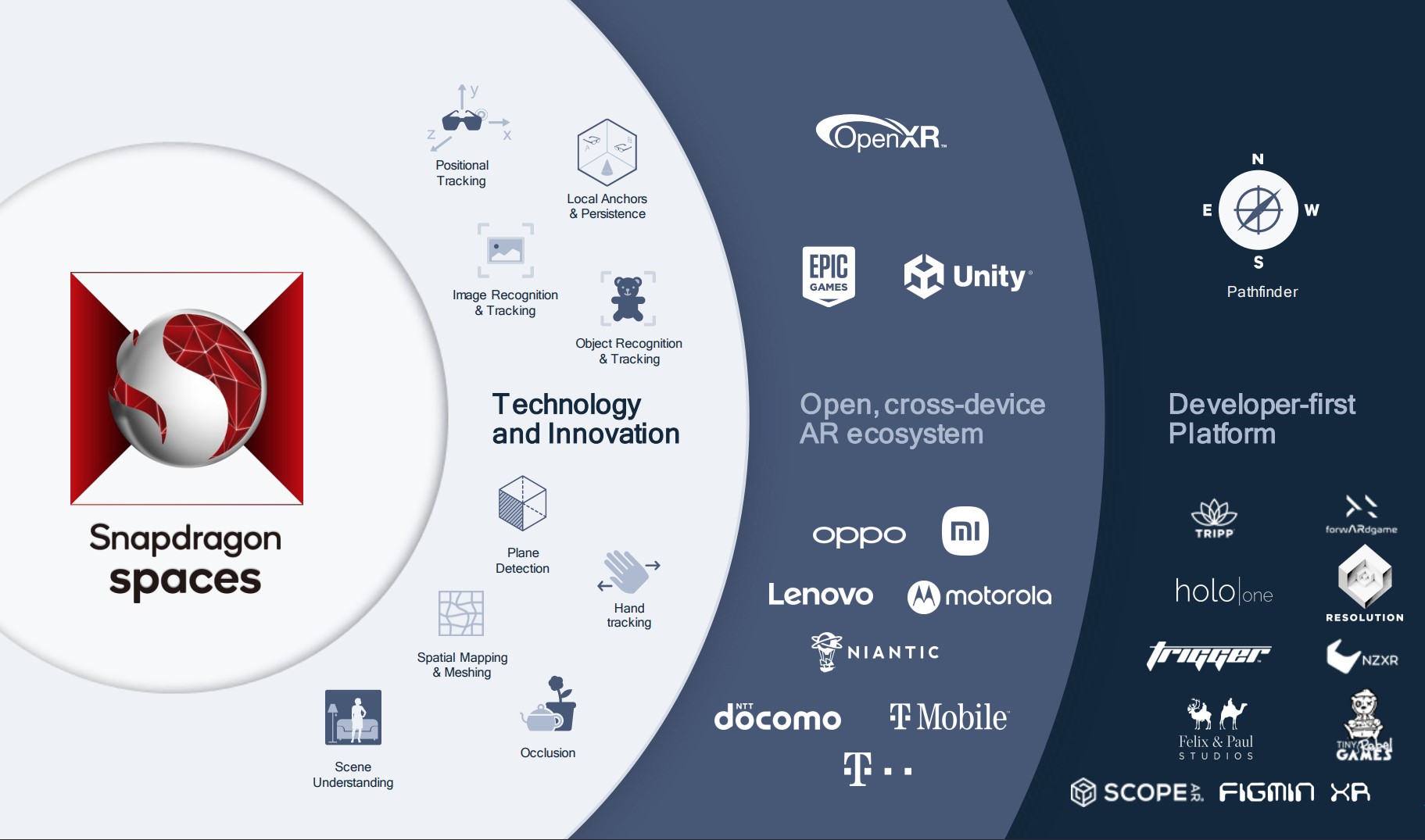
Qualcomm today launched a new developer platform for building head-worn augmented reality experiences: the Snapdragon Spaces XR Developer Platform. The only supported hardware for the platform is currently Lenovo’s ThinkReality A3 smart glasses (paired with a Motorola phone), but it will expand to include hardware from Oppo and Xiaomi in the first half of 2022.
To build out the software ecosystem, Qualcomm lined up a wide range of partners, including Epic Games’s Unreal Engine, Niantic’s Lightship platform, Unity, Viacom CBS and others. Deutsche Telekom and T-Mobile U.S. are also partnering with Qualcomm to support startups that use Snapdragon Spaces through the hubraum program.
For now, only a small number of developers will have access to the program. These currently include the likes of Felix & Paul Studios, holo|one, Overlay, Scope AR, TRIPP, Tiny Rebel Games, NZXR, forwARdgame, Resolution Games and TriggerGlobal. It plans to make the platform generally available in the spring of next year.
The company also today announced that it has acquired “the team and certain technology assets from HINS SAS and its wholly owned subsidiary, Clay AIR, Inc.” for its hand tracking and gesture recognition solutions. This is in addition to Qualcomm’s acquisition of Wikitude in 2019, another move that helped it jumpstart its AR efforts.
“Dating back to 2007, we had R&D programs, looking into augmented reality with algorithms like VIO [visual-inertial odometry] on smartphones,” said Hugo Swart, Qualcomm’s vice president and GM of XR, in a press briefing ahead of today’s announcement. “We enabled, through the last decade, devices like ODG. In 2014, we created new chips dedicated to virtual reality and augmented reality — and we are here for the long run. We know that we’re not there — it’s still going to require investment until we get to the holy grail of AR glasses that can do both fully immersive and augmented experiences.”
Today’s platform is able to support features like local anchors and persistence, hand tracking, object recognition and tracking, plane detection, occlusion spatial mapping and meshing.
With this platform, Qualcomm wants to lower the barriers for developers to build AR experiences. They will get access to documentation, sample code, tutorial and additional tooling to quickly build basic AR applications. To further help companies who want to build for this ecosystem, Qualcomm is also opening up an additional program, dubbed Pathfinder. With this, they will get early access software tools and hardware development kits, additional funding for their projects and co-marketing and promotion from Qualcomm.